개요
얼마전, 개발하면서 알게된 개념들을 wiki라는 repository에 markdown으로 정리하고, https://hoseungjang.github.io/wiki-front에서 해당 repository의 내용들을 읽어서 웹으로 시각화하는 프로젝트를 진행했습니다.
간단히 CRA로 initialize해서 개발한 후 Github Pages에 배포했는데, Github Pages는 SPA를 적용할 방법을 제공하지 않기 때문에 404 에러가 나오는 문제가 있었습니다.
처음에는 404.html을 사용한 트릭으로 해결했었지만, 이 경우 Open Graph protocol 데이터를 제대로 파싱하지 못하는 문제가 있었습니다.
이 글에서는 react-router의 HashRouter로 해당 문제를 해결했던 과정을 소개하겠습니다.
Hash Router
react-router의 Hash Router는 url의 hash를 활용한 라우터입니다.
아래와 같은 꼴로 url을 형성하고, window.location.hash를 파싱하여 동작합니다.
/#/example/1위의 경우, widnow.location.hash에 담긴 값은 "#/example/1" 입니다.
BrowserRouter와 동작, 사용법 모두 똑같습니다.
import { render } from "react-dom";
import { HashRouter, Switch, Route } from "react-router-dom";
render(
<HashRouter>
<Switch>
<Route path="/" component={/* ... */} />
<Route path="/login" component={/* ... */} />
</Switch>
</HashRouter>,
document.getElementById("root")
);또는, Router에 hash history를 넘겨서 사용할 수 있습니다.
import { createHashHistory } from "history";
import { render } from "react-dom";
import { Router, Switch, Route } from "react-router-dom";
const history = createHashHistory();
render(
<Router history={history}>
<Switch>
<Route path="/" component={/* ... */} />
<Route path="/login" component={/* ... */} />
</Switch>
</Router>,
document.getElementById("root")
);hash?
우선 hash가 뭔지 알아야 하는데, 일반적으로 url에서 hash는 페이지의 특정 요소를 참조하기 위해 사용합니다.
예를 들어,
/document#who-am-i로 이동하면, 브라우저는 html 내부에서 id가 who-am-i인 엘리먼트를 찾아 해당 위치로 스크롤해줍니다.
그리고 hash는 단순히 internal reference이기 때문에, hash값이 바뀌더라도 새로운 페이지를 요청하지 않습니다. 위 예시에서 hash 값을 아래와 같이 바꾼다고 해도,
/document#what-is-this엔드포인트는 hash를 제외한 /document 입니다.
따라서 Github Pages에 간편하게 SPA를 적용할 수 있습니다.
window.location vs useLocation()
HashRouter를 사용하는 경우, window.location을 참조하는 것과 useLocation()으로 current location 정보를 얻는 것은 완전히 다릅니다.
예를 들어, /#/document#who-am-i 로 이동했을 때 window.location과 useLocation()의 결과는 아래와 같습니다.
// window.location
{
pathname: "/",
hash: "#/document#who-am-i",
...
}useLocation()
{
pathname: "/document",
hash: "#who-am-i",
...
}즉, BrowserRouter를 사용할 때에는 window.location을 사용해도 차이가 없지만, HashRouter를 사용할 때에는 반드시 useLocation hook을 사용해야 합니다.
history가 변경되면 적절하게 scroll하기
BrowserRouter를 사용했다면 브라우저가 window.location.hash값을 읽어서 자동으로 스크롤을 해주었겠지만, HashRouter를 사용할 땐 개발자가 직접 스크롤하는 코드를 작성해야 합니다.
특히 위키 같은 서비스는 목차를 눌러서 자동으로 스크롤을 이동하는 기능이 필수적이기 때문에, 꼭 해줘야하는 작업입니다.
우선 react-router에서 제공하는 history 객체에는 listen() 메소드가 있는데, 이것을 사용해서 HashRouter의 history가 변경되었을 때 실행될 이벤트 리스너를 등록할 수 있습니다. (hash값의 변경도 history 변경으로 취급합니다.)
const history = useHistory();
useEffect(() => {
return history.listen(() => {
const targetElement = document.getElementById(decodeURIComponent(history.location.hash.slice(1)));
if (targetElement) {
window.scrollTo({ top: targetElement.offsetTop, behavior: "smooth" });
}
});
}, [history]);hash 값을 읽어서 엘리먼트를 찾은 후, 해당 엘리먼트의 위치로 스크롤하는 코드입니다.
마무리
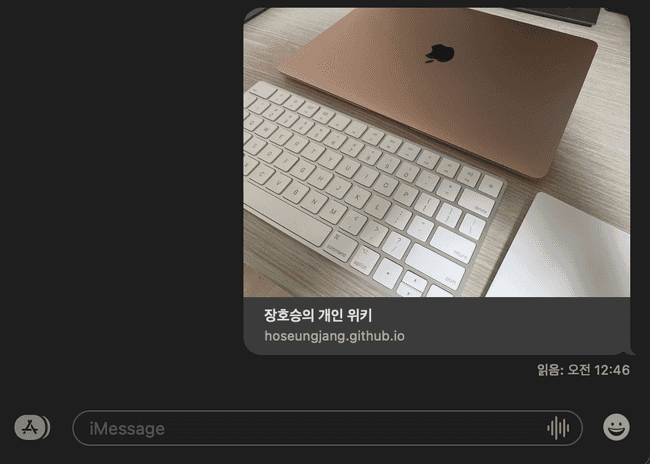
페이지를 이동해도 404 에러가 더이상 나오지 않았고, Open Graph 데이터를 파싱하지 못하던 문제도 아래 사진과 같이 해결된 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
전체 코드가 궁금하시다면 wiki-front를 참고해주세요.